Tips for Caring for Patients with Diabetes
November 30 2021
A Caregiver’s Checklist for Daily Care to Avoid Complications
Diabetes is a serious disease that requires lifelong care. Helping care for diabetes patients doesn’t just make them feel better or make life a little easier when it comes to daily tasks. It can actually help them avoid common diet, foot, and mouth issues.
Remember that many diabetes patients may already have their own daily routines. Some may only need reminders or prompts, while others may need much more help with their daily care routine.
General Daily Care Tasks
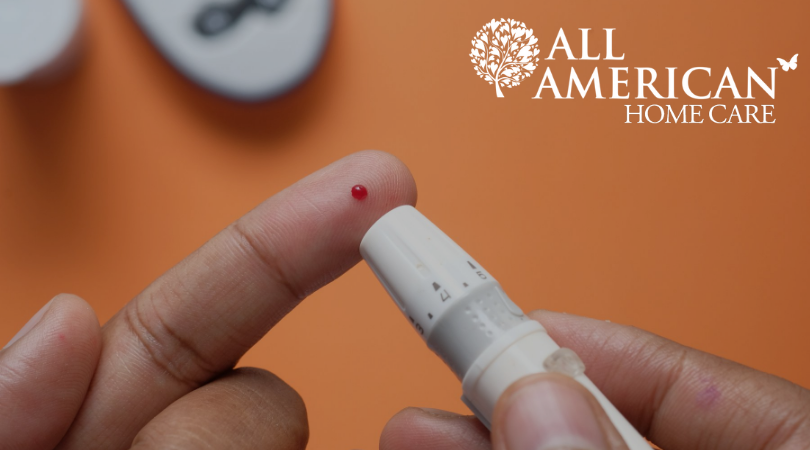
- Blood Glucose Readings: One of the most important things is to keep their blood sugar levels healthy. This will require keeping a daily record of blood glucose readings, medicine schedule, meals, exercise, and even how they feel. This can help the doctor look for patterns that might need to be addressed.
- Exercise: Getting in some exercise is part of a healthy lifestyle. However, it is key that diabetes patients wait an hour or so after eating, when blood sugar is likely higher. Be sure that your patient has glucose tablets or a carbohydrate snack plus plenty of water on hand when they exercise. They should also check their blood glucose before, during, and after exercise.
- Stress: Help your diabetes patients avoid stress as it can affect their blood sugar. To help ease stress they may be experiencing, they can take a walk, do deep breathing exercises, meditate, listen to music, or work on a hobby.
- Medications: Be sure they are taking their medicine or insulin, or monitoring their insulin pump and making adjustments as needed.
Grooming
- Mouth Health: Patients with diabetes are more likely to have mouth issues, such as gum disease, fungus or dry mouth. Ensure they are brushing their teeth with a soft-bristled brush after every meal and are flossing at least once a day.
- Toenails: Ingrown toenails can lead to infection and other problems. Check their toenails once a week for swelling or signs of infection. Toenails should be trimmed with nail clippers straight across and then smoothed with an emery board. Don’t round off nail corners.
Bathing
- Skincare: Use mild soap and warm (not hot) water while bathing to help prevent dry skin. Skip foot soaking, which can lead to dry skin between the toes. Afterward, use a doctor-approved moisturizer, including on their feet (except between the toes).
- Foot Care: Skip foot soaking and moisturizer between toes. Gently care for calluses by using a pumice stone or emery board, moving in one direction only. Promptly take care of any cuts on the foot that can lead to serious problems by washing with soap and water. If your patient has a cut, check it daily to make sure it is healing properly.
- Check for Sores: Nerve damage from diabetes may cause a loss of feeling in their feet and your patients may not even feel a cut or sore on their feet. Check their skin, especially their feet, daily for sores, blisters or red spots.
Dressing (Shoes and Protection for Feet)
- Shoes: As a general rule of thumb, diabetic patients should not wear sandals or go barefoot, even when just walking around the house. Soft leather, lace up shoes with cushioned soles for good support are a better option. Shoes and slippers should always have closed toes. Socks shouldn’t be too tight so they don’t hurt their circulation.
- New Shoes: If shoes are new, they should be broken in by wearing them for one or two hours. Check for cuts or blisters. Add a couple of hours each day and continue checking for issues until they feel comfortable. If they get a blister, do not pop it. Wash it with soap and water then apply an antibiotic cream. If it doesn’t heal in a few days, notify the doctor.
Eating
- Blood Sugar Levels: It’s extremely important for diabetics to keep their blood sugar levels as stable as possible. It’s better if they eat meals at the same time every day, with healthy snacks in between. Some patients may prefer to eat several smaller meals throughout the day. It is not a good idea for them to skip meals as this can cause a drop in their blood glucose.
- Diet: Be sure the patient is sticking to their meal plan created by the care team. Their diet will usually include portions of carbohydrates at every meal and a snack in between meals.
- Fluids: Diabetics should drink plenty of fluids throughout the day, such as water and caffeine free, sugar free drinks to keep their body and skin hydrated.
A Helping Hand
If you or a loved one has diabetes and needs help with daily care, our experienced and highly trained professionals are ready to help! We can help with everything from monitoring medication and insulin to wound care and meal assistance. Contact us today to learn more about how we can create an individualized care plan that will keep you or your loved one healthy and happy.





